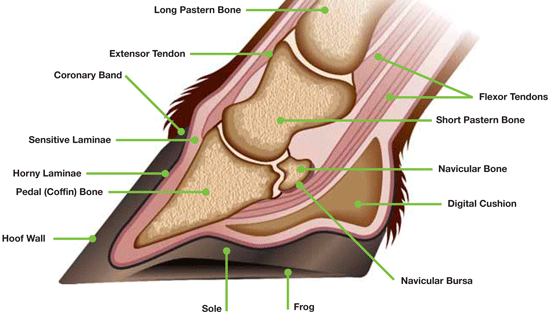
The classic hypothesis suggests that high levels of carbohydrate in the diet see subacute ruminal acidosis invoke an increase of streptococcus bovis and lactobacillus spp which induce a state of acidosis in the rumen.
What causes laminitis in cows.
Correct grain overload keeping the animal moving and the claws cool.
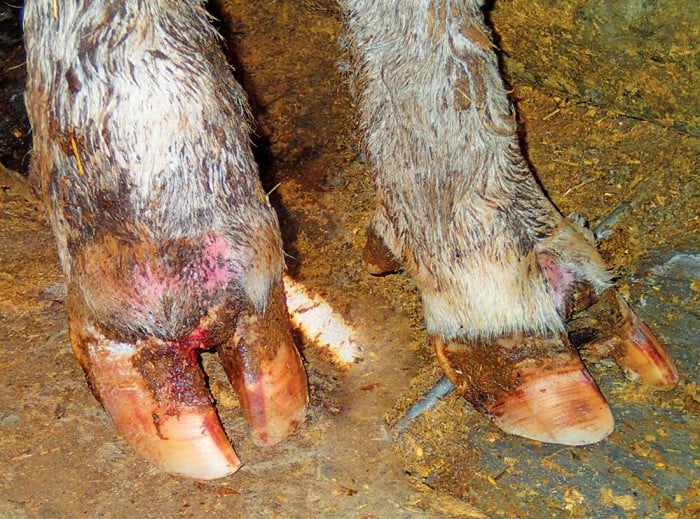
Today laminitis also known as founder is the main cause of lameness in cattle.
This causes gram negative organisms to die and release vasoactive endotoxins.
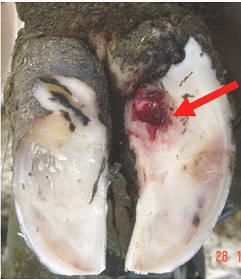
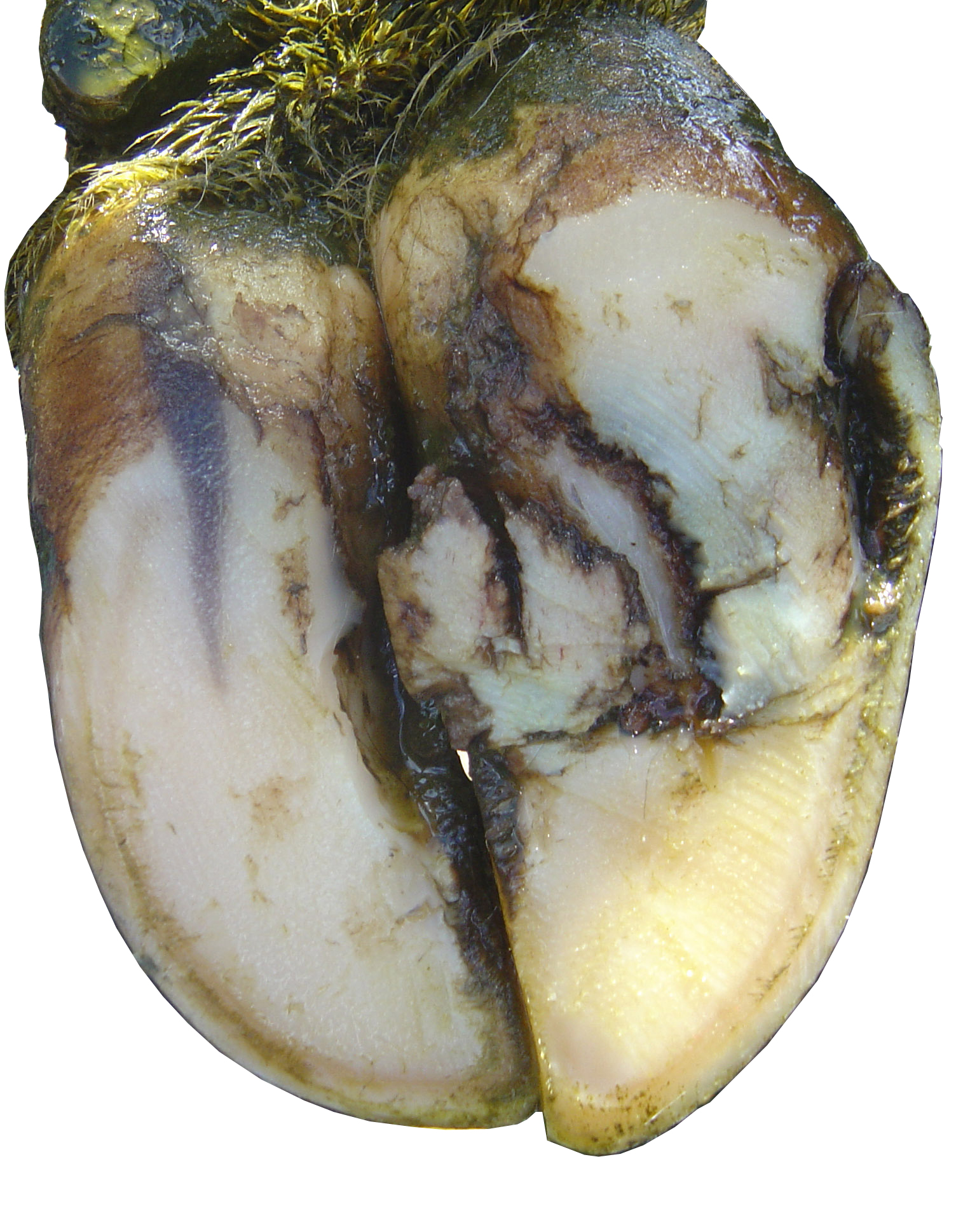
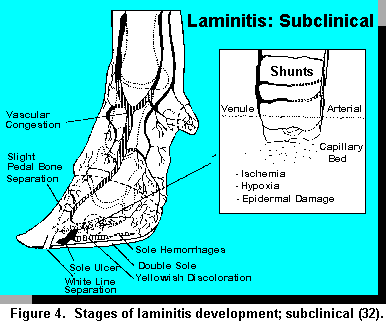
The etiology of subclinical laminitis in cattle is not understood.
Slatted floors can cause lameness in cattle due to injuries if the slats are fitted incorrectly or poorly maintained.
One of the more common causes current theory states citation needed that if a horse is given grain in excess or eats grass under stress and has accumulated excess nonstructural carbohydrates sugars starch or fructan it may be unable.
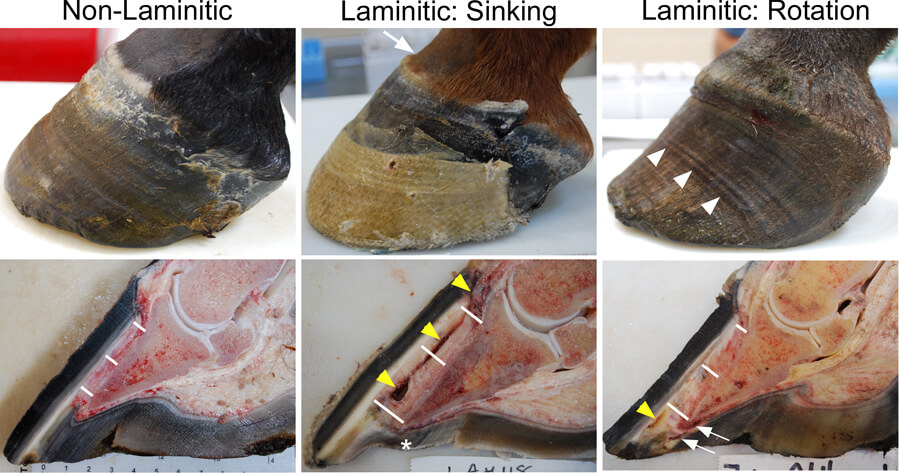
While the exact mechanisms by which the feet are damaged remain a mystery certain precipitating events can produce laminitis.
Cattle infected with mycoplasma bovis are at risk of joint infection.
Excessive protein levels in the diet unlikely in pasture based farming systems except at turnout onto fresh grass in spring are also known to cause laminitis.
Laminitis claw disease digital dermatitis and foot rot.
Antihistamines may be useful e g.
Thus laminitis has a great economic impact on dairy operations and all over the world dairy producers are moving towards housing cows in intensive confined conditions.
Dr chris clark of the western college of veterinary medicine discusses some of the many causes of lameness in cattle.
As we understand the causes of laminitis and identify the risk factors better it is possible to prevent and reduce the effects of the laminitis syndrome.
Heavier cattle or cattle held on feed for too long are at a higher risk for lameness.
Nsaid non steroidal anti inflammatory drug injectable ketoprofen 2 to 4 mg kg im iv.
The most frequent causes of lameness are.
High grain rations erratic feed consumption due to weather factors or feed supply problems and improper feed processing are risk factors for laminitis.
Injectable diphenhydramine 0 5 to 1 0 mg kg iv im.
Although laminitis occurs in the feet the underlying cause is often a disturbance elsewhere in the horse s body.
Since individual cows often have more than one cause for lameness at the same time it is important to understand the different types of lameness as well as the treatment and prevention protocols.
These causes can be grouped into broad categories.