This is the silica rich magma that is often violently expelled from the large volcanos like mt.
What is granitic magma rich in.
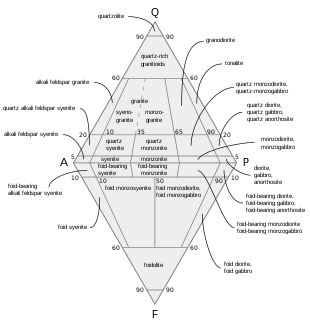
Granite ˈ ɡ r æ n ɪ t is a common type of felsic intrusive igneous rock that is granular and phaneritic in texture.
Consequently a chemical classification is widely accepted and employed by most petrologists.
Owing to the aphanitic texture of volcanic and hypabyssal rocks their modes cannot be readily determined.
First of all you should know the difference between lava and magma magma and lava are both molten liquid rock but magma is moltenrock produced underneath earth surface while it magma erupts on the surface of earth it is called lava.
One popular scheme is based on the use of both chemical components and normative mineralogy.
Magma or hot molten rock beneath the earth s surface has an average temperature of around 1300 degrees f to 2400 degrees f or 700 degrees c to 1300 degrees c.
The issue of the origins and evolutionary mechanisms of granitic magmas is a vast subject.
The debates centred on the rocks of this region closely mirror those current in most other granite rich regions of the continental crust.
As the k feldspar granites represent the residual crystal mush the ba isotope data of the coexisting ba bearing minerals can impose critical constraints on crystal melt separation.
Rainier which sit above subduction zones today.
Komatiite magma in particular can reach the temperature of 1600 degrees celsius.
Saint helens and mt.
Magma formation depends on the type of environment it is formed.
The resulting magma is less dense than material typically found at that depth so it rises like oil in salad dressing.
Strictly speaking granite is an.
Learn more about the properties and uses of granite in this article.
Igneous rock igneous rock classification of volcanic and hypabyssal rocks.
Trace element modeling suggests that such variations can be explained by k feldspar controlled crystal melt separation in a k rich granitic magma.
It is the most common plutonic rock of the earth s crust forming by the cooling of magma silicate melt at depth.
Granite coarse or medium grained intrusive igneous rock that is rich in quartz and feldspar.
The focus on the lfb is appropriate as this is the type locality for s and i type granites.